United SNMP Collector Introduction
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
The ElastiFlow Unified SNMP Collector is more than a simple SNMP poller. It has been designed to meet the requirements of the most demanding production environments, with particular attention on the following attributes:
Turnkey
The SNMP Input puts an end to countless hours of building polling configurations, and the error-prone copy-pasting necessary to poll new devices, which is required of other solutions. SNMP MIB attributes must be defined only once and can be flexibly referenced by the devices to which they are applicable.
The input includes a growing collection of out-of-the-box MIB Object definitions, as well as Object Groups and Device Groups, which make it quick and easy to get started polling your environment. This enables the collector to understand how to poll a Juniper EX-Series differently than a Cisco Catalyst. Adding a device is as simple as providing an IP address, credentials and one or more Device Groups, e.g. juniper_ex.
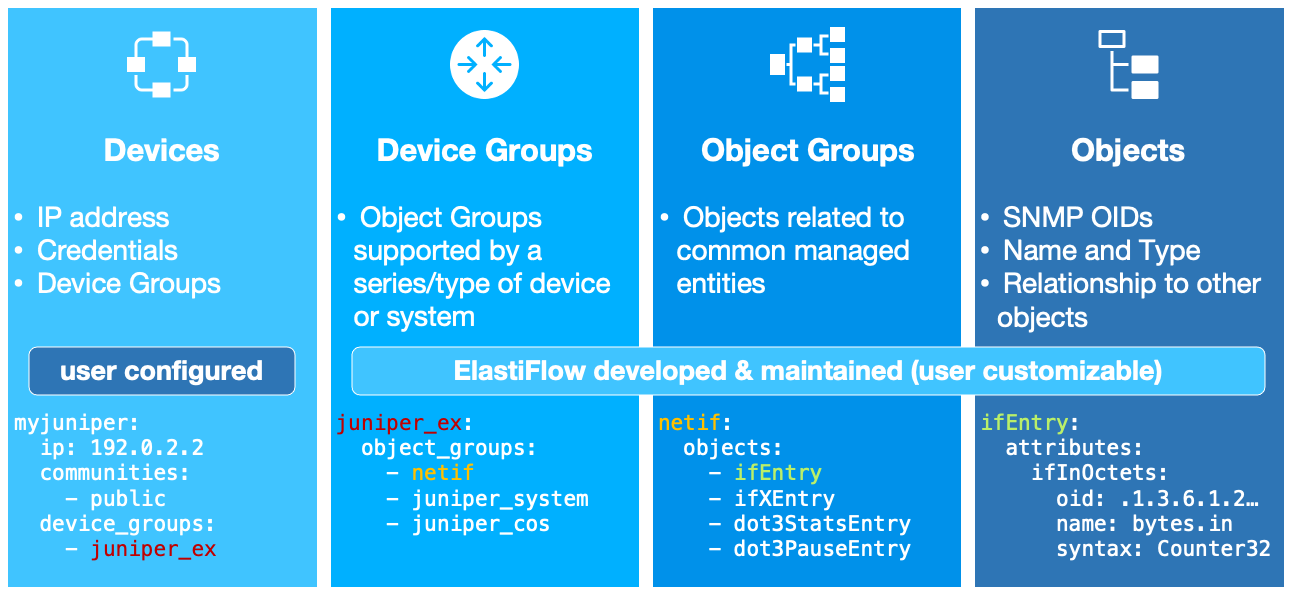
Extensible
The SNMP Input includes pre-built support for some of the most popular network equipment, which will continue to grow in the future. However there will always be new, rare or custom devices which are not yet part of our pre-built options. In this scenario, it is easy for users to add configurations or even modify existing definitions.
Efficient
The key to using SNMP with a minimal impact on network bandwidth and device resources is efficient polling. The SNMP Input achieves this by first performing a low-touch discovery of Objects applicable to the target device. The resulting SNMP object inventory is leveraged by the scheduler to poll devices in the most efficient manner possible. It is not uncommon for the input to collect 50 or more OIDs in a single poll. This greatly reduces the number of packets sent out over the network, as well as the load on the limited resources found in many devices.
Adaptive
It isn’t uncommon for devices to be reconfigured or restarted for maintenance or other operational requirements. The SNMP Input can respond dynamically to detected changes, modifying the polling schedule to remove objects and attributes which are no longer available, or automatically trigger a rediscovery when warranted by a device’s new state.
Scalable
ElastiFlow has proven itself as perhaps the most scalable Flow Collector available, especially when considering its depth of processing and features. The SNMP Input provides this same level of scalability by:
Leveraging a large (and configurable) pool of concurrent poller workers.
Taking advantage of the same processing techniques and outputs as the Flow input.
Enabling SNMP Collection
To enable the SNMP Input, refer to the configuration reference HERE. Devices can be added as explained HERE.